Marketers and community managers who work with social networks are often tempted to use social publishing optimization tools. Yet, the recipe behind such tools is often obscure for non-data scientists. Here are a few tips to shed light on recipes used to optimize your social posts.
1. Semantic Analysis
Publishing optimizers have a database of historical data from existing posts used for analysis. First, they can scan the words in these posts. In order to do so, they can implement two different types of semantic analysis.
1. They can analyse the format of the post: length, length of sentences, word characteristics (presence of technical words, sentence structures…)
2. They can analyse the concept of the post: finding keywords or key sentences attached to concepts in order to figure out what the content of the post is. To do so, optimization tools work with sequences of words, for instance ‘information technology’, ‘open innovation’, ‘connected device’, etc.
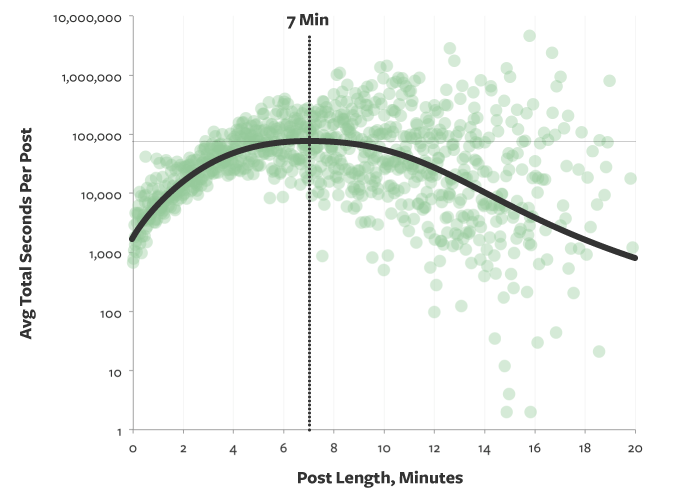
The ideal length for a blog post is 7 minutes of reading time, which is equivalent to 1,500 words (or less for an image-rich blog post). This post is roughly 500 words long. You know the proverb about the shoemaker always walking barefoot :)
2. Image Analysis
As far as pictures are concerned, optimization tools analyse a certain number of factors such as colorimetry, contrast, the presence of certain colours, or the presence of faces on pictures. These elements are taken into account when assessing if a picture can have a positive impact.
3. Comparison
All the information is then compared with data from previous posts: occurrences of word sequences in previous articles, at what time they were posted, at what speed they have been viewed, or how many times they were included in other blogs, Facebook posts, or tweets. Buzzwords such as "big data" might be so frequent that they are loosely correlated with success. Better discard them, then.
4. Magic
Eventually, each provider has a “magic formula”, i.e. a specific algorithm. Generally, providers use academic algorithms such as Random Forest, neural networks, or Support Vector Machine. What will make the difference is the richness of the variables selected, e.g. texts, trends, etc.
The Cherry on the Cake
The success of a post will rely on finding the proper mix between the right type of article, the right picture, the right time of day, the right literary complexity, and the right topic. Optimization tools will be able to spot improvement methods: make the text shorter or lighter, add trending keywords, change the time of publication, etc.
Get more insights on how to use machine learning for marketing in our guidebook.




